How to operate a drone safely and effectively opens up a world of exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to innovative applications across various industries. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and legal considerations. Whether you’re a complete beginner or looking to refine your skills, this resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to take flight responsibly.
We’ll explore the essential aspects of drone piloting, including understanding your drone’s controls, navigating using GPS, capturing high-quality aerial media, and performing routine maintenance. Crucially, we’ll also address the vital importance of adhering to all relevant safety regulations and legal requirements to ensure both your safety and the safety of others. By the end of this guide, you’ll possess the fundamental skills and awareness necessary to become a responsible and proficient drone operator.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and limitations. Learning the basics, such as takeoff and landing procedures, is crucial before attempting more complex maneuvers. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects from pre-flight checks to advanced flight techniques, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. Mastering these skills ensures safe and effective drone operation, maximizing your aerial experience.
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
Before each flight, a thorough pre-flight inspection is crucial for ensuring safe and successful drone operation. Neglecting this step can lead to accidents, equipment damage, and potential legal issues. This section details a comprehensive checklist and safe takeoff and landing procedures.
Pre-flight Inspection Importance
Pre-flight inspections are paramount for identifying potential problems before they cause incidents during flight. This minimizes risks and ensures the drone’s optimal performance.
Comprehensive Pre-flight Checklist
This checklist covers key aspects to inspect before every flight. Remember to adapt it to your specific drone model.
| Checklist Item | Inspection Method | Acceptable Result | Unacceptable Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| Battery Level | Check the battery indicator on the drone and remote | Battery level at or above recommended minimum for flight time | Battery level below recommended minimum; charge battery |
| Propeller Condition | Visually inspect each propeller for cracks, chips, or damage | All propellers are intact and free from damage | Replace damaged propellers |
| GPS Signal | Observe the GPS indicator on the remote controller | Solid GPS signal with sufficient satellites acquired | Weak or no GPS signal; relocate to an area with better reception |
| Gimbal Function | Check the camera gimbal movement | Gimbal moves smoothly and accurately | Gimbal is stiff or unresponsive; check connections and settings |
| Remote Control Connection | Check the connection between the drone and remote controller | Strong signal connection with no dropouts | Weak or intermittent connection; check batteries and interference |
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedure

Follow these steps for a safe and controlled takeoff and landing.
- Power on the remote controller first, then the drone.
- Wait for the GPS signal to lock.
- Perform a pre-flight calibration if required by your drone.
- Slowly lift off vertically, maintaining a steady ascent.
- For landing, descend slowly and smoothly, maintaining control.
- Power off the drone first, then the remote controller.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding your drone’s controls and navigation systems is essential for safe and effective operation. This section explains the functions of common controls and different flight modes.
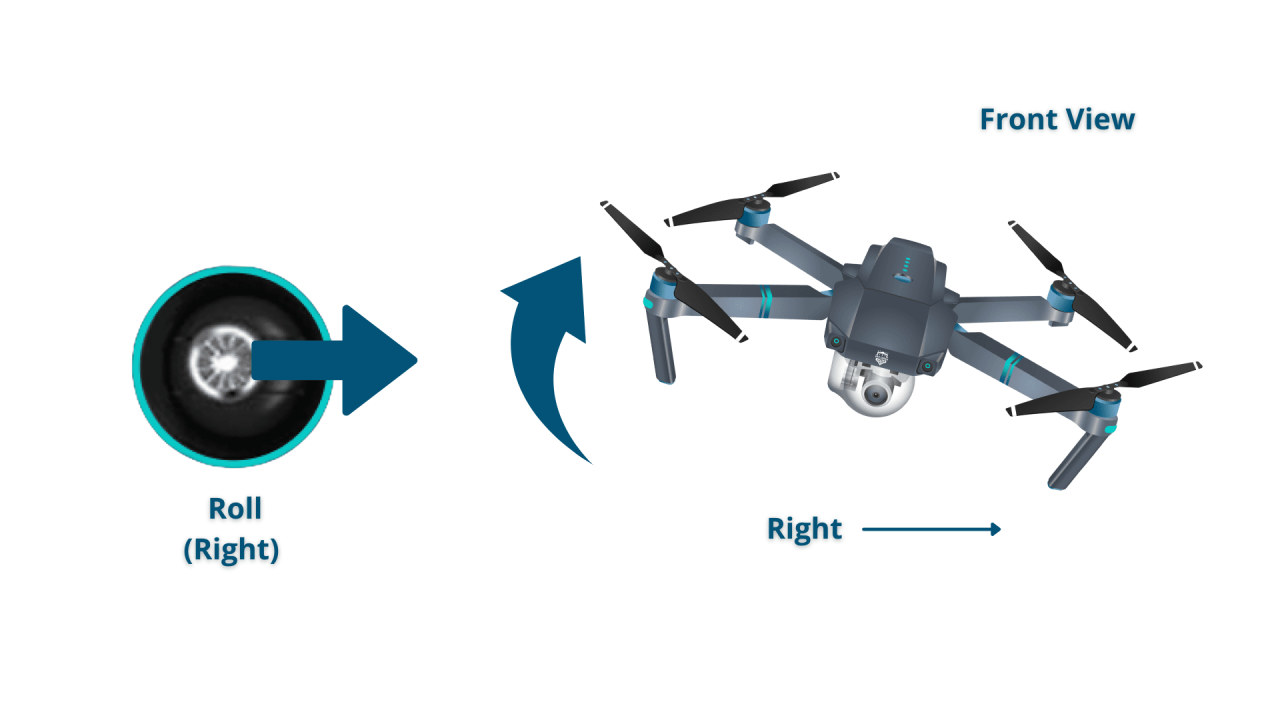
Drone Controller Functions, How to operate a drone
Most drone controllers feature two joysticks. The left joystick typically controls altitude and yaw (rotation), while the right joystick controls the drone’s forward/backward and left/right movement. Buttons on the controller typically manage camera functions, return-to-home, and flight mode selection.
Flight Modes
Different flight modes offer varying levels of control and stability. Beginner mode limits speed and responsiveness, while sport mode allows for more agile maneuvers. Understanding the implications of each mode is critical for safe operation.
GPS Navigation
Many drones utilize GPS for precise positioning and navigation. This allows for automated functions like return-to-home and waypoint navigation. Pilots can input GPS coordinates or create waypoints to guide the drone along a pre-determined path.
Return-to-Home Flowchart
The following flowchart illustrates the steps involved in returning a drone to its home point.
The flowchart would show a sequence of steps: Initiate RTH command, Drone confirms command, Drone assesses GPS signal, Drone initiates flight path calculation, Drone begins autonomous flight back to home point, Drone performs landing sequence at home point, Drone confirms landing, RTH sequence complete.
Taking High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
Capturing stunning aerial footage requires understanding camera settings, lighting conditions, and composition techniques. This section offers tips for improving image and video quality.
Tips for Sharp, Stable Images and Videos
Use a tripod or gimbal for stability, choose optimal lighting conditions, and adjust camera settings such as ISO, shutter speed, and aperture to suit the environment. Experiment with different camera angles and movements for dynamic footage.
Impact of Lighting and Camera Settings
Lighting significantly impacts image quality. Avoid harsh midday sun, which creates strong shadows and overexposure. Experiment with the golden hour (sunrise and sunset) for softer, more flattering light. Proper camera settings (ISO, shutter speed, aperture) are crucial for achieving sharp, well-exposed images and videos. A lower ISO reduces noise, a faster shutter speed minimizes motion blur, and adjusting the aperture controls depth of field.
Camera Angles and Effects
Different camera angles create distinct visual effects. High-angle shots provide a wide overview, while low-angle shots emphasize the subject’s scale and grandeur. Side shots offer a different perspective. Experimentation is key to finding the best angles for your specific needs.
Understanding drone operation involves several key aspects, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Learning the fundamentals is crucial for safe and effective flights; for a comprehensive guide, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone which covers everything from basic maneuvers to advanced techniques. Proper training ensures you can confidently and responsibly operate your drone.
Common Drone Photography Mistakes
- Ignoring lighting conditions: Plan your shoots around optimal lighting.
- Using incorrect camera settings: Adjust settings to match lighting and desired effect.
- Neglecting stability: Use a gimbal or other stabilization methods.
- Flying too close to the subject: Maintain safe distance for better perspective.
- Not planning shots: Pre-visualize your shots for better results.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting skills are essential for keeping your drone in top condition and resolving issues quickly. This section provides guidance on both.
Regular Maintenance Schedule
Clean the drone’s body and propellers after each flight. Inspect for any damage or wear and tear. Store the drone in a dry, safe place away from extreme temperatures.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Common issues include low battery warnings (low battery charge), GPS signal loss (interference or weak signal), and motor malfunctions (mechanical issues or software glitches). Understanding potential causes aids in effective troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting Steps

For low battery warnings, charge the battery fully. For GPS signal loss, relocate to an area with better reception. For motor malfunctions, check for physical obstructions and ensure proper connections. Consult your drone’s manual for more specific troubleshooting guidance.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Troubleshooting Steps | Prevention Tips |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Battery Warning | Low battery charge | Charge the battery fully | Monitor battery level during flight and land before critical low level |
| GPS Signal Loss | Interference or weak signal | Relocate to an area with better reception | Fly in open areas with clear sky visibility |
| Motor Malfunction | Mechanical issues or software glitches | Check for physical obstructions, inspect motor connections, reboot drone | Regularly inspect motors for damage, keep drone clean |
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to all relevant laws and regulations. This section provides an overview of key considerations.
Key Regulations and Laws
Regulations vary by region. Before flying, research and understand the specific rules in your area. These often include registration requirements, airspace restrictions, and limitations on flight time and altitude.
Permits and Licenses
Depending on your location and intended use, you may need permits or licenses to operate a drone. These are often required for commercial use or flights in restricted airspace.
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Certain areas are restricted to drone flights, including airports, military bases, and national parks. Failing to comply can lead to penalties.
Prohibited Scenarios
Operating a drone near emergency situations, over crowds, or without proper authorization are examples of prohibited scenarios. These restrictions are in place to ensure public safety and prevent accidents.
Advanced Drone Techniques
This section explores advanced drone maneuvers, features, and simulation software for enhancing piloting skills.
Complex Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers such as flips, rolls, and precision hovering require practice and skill. Start slowly and gradually increase the complexity of your maneuvers.
Advanced Flight Features
Features like obstacle avoidance and follow-me mode enhance safety and convenience. Obstacle avoidance helps prevent collisions, while follow-me mode allows the drone to automatically track a moving subject.
Drone Simulation Software
Simulation software allows for practicing maneuvers in a risk-free environment. This helps improve skills before attempting them in real-world flights.
| Drone Model | Features | Price (USD) | Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| DJI Mavic 3 | 4K video, obstacle avoidance, long flight time | 2000 | Aerial photography, videography, mapping |
| Autel EVO II Pro | High-resolution camera, long range, multiple flight modes | 1500 | Aerial photography, videography, inspection |
| Parrot Anafi USA | Compact design, 4K HDR video, 180° tilting camera | 800 | Aerial photography, videography, travel |
Illustrative Examples of Drone Applications: How To Operate A Drone
Drones are increasingly used across various sectors. This section provides examples of their applications in agriculture, construction, and search and rescue.
Drone Use in Agriculture
In agriculture, drones are used for crop monitoring, assessing plant health, and targeted pesticide application. They provide valuable data for optimizing farming practices and increasing yields. For example, a farmer might use a drone equipped with a multispectral camera to identify areas of stress in a field of corn, allowing for targeted intervention before widespread damage occurs.
Drone Use in Construction
In construction, drones are employed for site surveying, progress monitoring, and inspection of structures. They provide detailed imagery and data for planning, progress tracking, and identifying potential problems. For example, a drone could be used to create a 3D model of a construction site, allowing for better planning and coordination of tasks. Progress can be easily tracked over time through comparison of sequential images.
Drone Use in Search and Rescue
Drones are invaluable in search and rescue operations, providing aerial surveillance and assisting in locating missing persons or victims of disasters. Their ability to cover large areas quickly and provide real-time imagery is critical in time-sensitive situations. For example, a drone equipped with thermal imaging could be used to locate a missing hiker in a wooded area at night, significantly improving the chances of a successful rescue.
Descriptive Text for Drone Application Images
Image 1: A drone hovers over a lush green field, its camera capturing detailed images of the crops. The high-resolution imagery reveals variations in plant health, highlighting areas needing attention. The image showcases the precision and efficiency of drone-based crop monitoring.
Image 2: A drone flies over a bustling construction site, capturing a panoramic view of the project. The image displays the intricate details of the construction process, from the foundations to the nearly completed structure. This perspective provides valuable data for progress tracking and quality control.
Image 3: A drone equipped with a thermal camera soars above a rugged terrain, its infrared sensors detecting heat signatures. A faint heat signature, representing a potential survivor, is visible amidst the landscape. This image highlights the crucial role of drones in search and rescue missions.
Mastering the art of drone operation is a journey of continuous learning and responsible practice. From the initial thrill of takeoff to the satisfaction of capturing stunning aerial footage, operating a drone offers a unique and rewarding experience. By diligently following the safety guidelines, understanding the legal framework, and consistently practicing your skills, you can unlock the full potential of this remarkable technology while ensuring the safety and enjoyment of your flights.
Remember that responsible operation is paramount, and continued learning is key to becoming a skilled and proficient drone pilot.
Helpful Answers
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with beginner modes are available. Look for features like GPS stabilization, automatic return-to-home, and obstacle avoidance.
How long does a drone battery last?
Flight times vary greatly depending on the drone model and battery size. Expect anywhere from 15-30 minutes on a single charge, though some larger models offer longer flight times.
What happens if I lose the GPS signal?
Most modern drones have a return-to-home function. If the signal is lost, the drone will attempt to return to its takeoff point. However, always maintain visual contact with your drone.
How do I register my drone?
Registration requirements vary by country and region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific rules and regulations.
